Color Vision Deficiency (CVD, formerly known as colorblindness) is a specific visual disability where a person can’t see the full color spectrum that post people can see. 1.
Approximately 4.5% of the world population have some form of CVD 2. It affects 1 in 12 men and 1 in 200 women 2. These figures are higher for white (Caucasian) people or others who have mixed race genes in their genetic history 2. If your company is bigger than 20 people, there’s a strong chance at least one of your co-workers is color blind.
More than a few kinds of CVD exist, each with its own challenges.
- Protanomaly is a reduced sensitivity to red light (1% of men) 3. Protanopia is the total inability to see red (1% of men) 3.
- Deuteranomaly is a reduced sense of green light (and the most common form of CVD, 5% of men) 3. Deuteranopia is the total inability to see green (1% of men) 3.
- Tritanomaly is a reduced sensitivity to blue light (and is extremely rare) 3. Tritanopia is the total inability to see blue 3. (Put together they’re about 1 in 30,000-50,000 people.)
- Achromatopsia is the extremely rare (1 in 33,000 people) form of colorblindness where there is no color, only monochromatic (shades of grey) vision 3.
People with either deuteranomaly or protanomaly are collectively known as red-green colorblind because regardless of which of the two types they have, they have difficulty distinguishing between red and greens, as well as browns and oranges. They may also confuse blues and purples 3
Design considerations
Don’t use color alone to communicate information. Ensure that your software passes WCAG 1.4.1 Use of Color – Level A 1.
Own voices
What people with CVD say about themselves.
- Color Blind Probs is a twitter account with a CVD author who retweets problems other CVD people have navigating the world.
- On Smells and Colors by Dan Brown is about Dan’s inability to smell (called anosmia) and his son’s CVD. Dan compares the challenges that each disability provides, and talks about how his son’s struggles have helped him understand both disabilities better.
- From A Colourblind Designer To The World: Please Stop Using Red And Green Together by Andrew Wilshere.
- Chasing Rainbows by Andy Bao.
What causes CVD?
CVD occurs when a person is unable to detect light at certain wavelengths.
Normal (human) vision uses three different cone cells in the eye to detect colors in specific light spectrums that roughly align to red, blue, and green light waves 4. If one or more of those cone types isn’t present or is malfunctioning, the person’s light spectrum is affected 4.
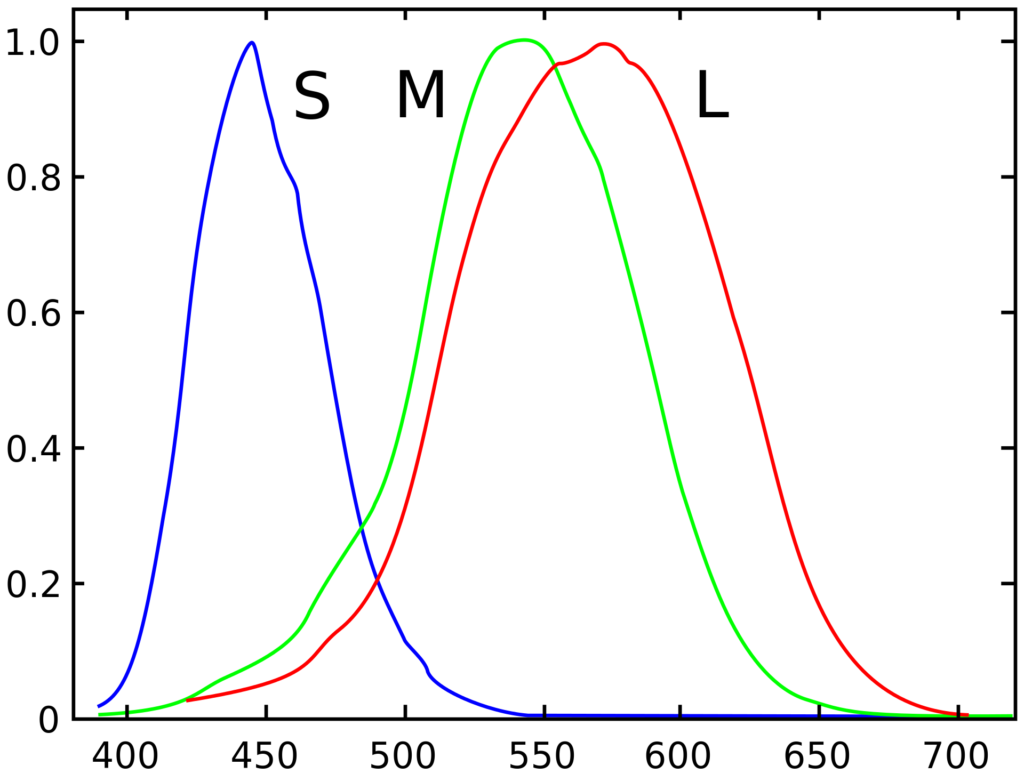
- Dichromacy is what happens when one of the three cone types is missing or damaged 5. This includes those with protanomaly, protanopia, deuteranomaly, deuteranopia, tritanomaly, and tritanopia 5.
- Monochromacy is what happens when two of the three types of cones are missing or damaged 6.
The majority of people inherit CVD from their mother 7. Others may become colorblind from other diseases such as Diabetes or from aging or certain medications 7. Damage to the cerebral cortex of the brain could cause cerebral achromatopsia where people are aware of their visual experiences but are unable to imagine or remember colors 8.
There are some people whose color vision is actually enhanced above normal.
- Tetrachromats have an extra set of cones that pick up more color between red and green than the usual trichromatic eyesight that most humans have 9.
Benefits of CVD
As with most disabilities, CVD is only a disability when the surrounding environment doesn’t align with a user’s experience. There may be some benefits to CVD.
- The US Army has reported that people with CVD could better spot people or things in camouflage than those with normal color vision ((Color Blindness or Color Vision Deficiency by Gianni A. Sarcone at Archimedes Lab).
- CVD may result in differences in texture or brightness more apparent. (The author posts an example picture on the page.) ((Color Blindness or Color Vision Deficiency by Gianni A. Sarcone at Archimedes Lab).
Tools
- Colorblind Web Page Filter by Toptal
- Check My Colours – will provide feedback on a color palette for CVD users
- I Want To See Like The Color Blind – will provide CVD filters through Chrome.
- Color Oracle – a CVD simulator for Windows, Mac, and Linux
- Colorsafe – provides accessible color palettes using a web tool
Additional resources
- Color Blind Awareness website provides information on CVD including types of CVD.
- Responding to Color by the Cooperative Extension Service of the University of Kentucky.
- 5 ways to design for people who are colorblind by Arkajyoti Das at the UX Collective
- Accessibility Fundamentals – Disabilities, Guidelines, and Laws at Deque University[↩][↩]
- About Colour Blindness by Colour Blind Awareness[↩][↩][↩]
- Types of Colour Blindness by Colour Blind Awareness[↩][↩][↩][↩][↩][↩][↩][↩]
- Cone cells by Wikipedia[↩][↩]
- Dichromacy by Wikipedia[↩][↩]
- Monochromacy by Wikipedia). It includes those with achromatopsia ((Monochromacy by Wikipedia).
- Color Blindness by Wikipedia[↩][↩]
- Cerebral Achromatopsia by Wikipedia[↩]
- Tetrachromacy by Wikipedia[↩]
There are other people who have significant difficulty distinguishing red from black, making red-on-black or black-on-red combinations difficult to discern ((Accessibility Fundamentals – Disabilities, Guidelines, and Laws at Deque University[↩]